Authors
Madison Aune
What are VpCIs?
VpCIs are a good choice for corrosion protection in enclosed void spaces. These inhibitors protect the metal surface by utilizing vapor technology to reach and protect hard to access areas, ensuring metal surface protection. VpCI molecules can travel wherever oxygen molecules can, making them highly effective for protecting crevices and other difficult to reach areas. By blocking moisture, oxygen, and other corrosive elements, VpCIs prevent oxidation and protect the system from damage.
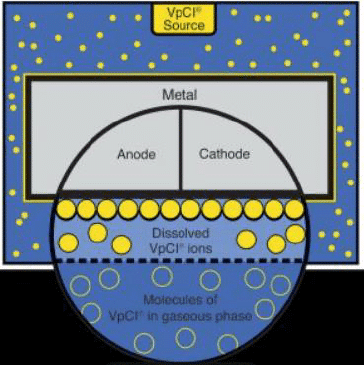
How Do VpCIs Work?
The polar nature of VpCI molecules is what makes them effective at protecting metals. These molecules have polar functional groups that are attracted to the charged surfaces of metals. This attraction allows the VpCI molecules to align and adhere to the metal surface. VpCI molecules release vapor and diffuse through the air, reaching micro-cavities of the metal. This results in a adsorption between the VpCI molecules and the metal, forming a monomolecular layer that prevents moisture, oxygen, and other corrosive elements from reaching the metal. This layer displaces water molecules, and protects against corrosion. As dipoles, VpCIs protect both the anodic and cathodic areas of the metal surface. VpCI technologies protect multiple metal types and work in multiple phases (liquid, vapor, and interface), so they can be used to inhibit corrosion on metal surfaces below and above the fluid level. VpCIs are released from their carrier material (e.g., liquid or powder) depending on the type of lay-up and system for which they are intended. These products could be applied to the system during different types of layups: dry, wet, or wet-dry. The choice of carrier material and application method ensures that the VpCI technology works effectively in reaching and protecting the metal surface to provide corrosion inhibition in the system.
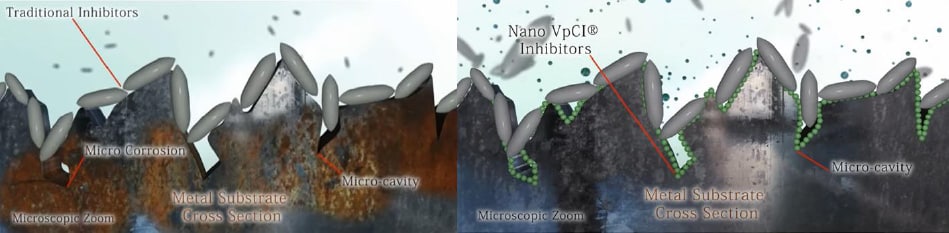
Figure 2. The visual difference between average corrosion inhibitor treatments (left) versus using VpCI technology (right) as a corrosion inhibitor.
Advantages of VpCI Technology
VpCI technology has many advantages including effective corrosion protection, ease of application, and environmental benefits. Cortec corporation, our preferred supplier of VpCI technology, is headquartered in St. Paul, MN. Many Cortec VpCI products are also recyclable or water-based and typically have a lower environmental impact than other water treatment chemicals. Applying Cortec products is straightforward and convenient. Unlike traditional rust preventatives, VpCIs do not need to be removed before the system is put back online. This advantage saves time, reduces labor, and reduces cost associated with cleaning and degreasing.
What Is A Layup?
A layup is a process of preparing and preserving boilers or cooling systems during periods of inactivity. Layups are designed to permit the boiler to remain at ambient conditions for long periods of time without creating corrosion problems, and also to expedite a rapid return to service.
The type of layup depends on the anticipated outage. If the unit is expected to be out of service for months or longer, dry layup should be used. For shorter outages, wet layup is recommended. The advantages of a layup are a minimization of corrosion, however the main disadvantages are the cost and time required to refill and startup.
Wet Layup: The system is filled with treated water and chemicals are circulated periodically to prevent corrosion.
Dry Layup: The system is completely drained of water, and drying agents are used to remove any remaining moisture and then sealed.
Wet-Dry Layup: Initially the system is treated with chemicals and filled with water. Before bringing the system online, it is drained and dried.
Boilers
To plan for VpCI application in your boiler, start by defining the scope of the layup. Determine the product option and amount needed for your system. Identify the best location(s) to place the product and arrange to take pictures for documentation. Here are the descriptions for using two Cortec boiler products.
Boiler Lizard: To begin, remove and discard the outer bag. Lay the product inside the boiler and slit the bag, leaving 2 inches on either end. Lastly, seal all openings to the boiler internals and close all valves. Do not use on copper alloys; the VpCI chemistry is not compatible with yellow metals.
Boiler Gecko: To start the procedure, seal all but two openings on opposite ends of the system. Fog the product in one end until it begins to fog out the second opening. Continue fogging until recommended dose is achieved. Seal all openings to the boiler internals and close all valves. This product and process is effective for all components of the boiler (e.g., pipes, boiler, valves).
Cooling Towers/Closed Loops
There are many reasons why you should layup a cooling water system. It reduces chip scale, flash corrosion, iron and microbial fouling. Treating the system can extend equipment life, eases start up, and has overall better ROI.
To prepare your cooling tower for VpCIs, start by physically cleaning the tower. Next, add a non-oxidizing biocide to the system. Afterwards, shut down bleed and circulate for 24 hours. Once the 24-hour period is complete, bleed the system.
To maintain the system, add your selected preservation product and circulate it for 12-24 hours. Once this is done, drain the system completely or partially. The system is now preserved. If the system needs to be put back online, repeat the process before taking it out of operation again.
